What is the difference between low-smoke halogen-free wires and flame-retardant wires?
 Update Time:2025-12-14
Update Time:2025-12-14
 Traffic:
Traffic:
Low-smoke halogen-free wires and flame-retardant wires are two types of wires with different characteristics. The main differences are reflected in materials, combustion characteristics, environmental performance and application scenarios. The following is a detailed comparison:
1. Definition and materials
Low smoke halogen-free wires:
Definition: The insulating layer does not contain halogen (F/Cl/Br/I/At) and heavy metals such as lead, cadmium, chromium, and mercury, and does not produce toxic substances such as hydrogen halide and carbon monoxide during combustion. It is a high-safety and environmentally friendly wire.
Material: Halogen-free polymer (such as cross-linked polyethylene XLPE), inorganic flame retardants such as aluminum hydroxide/magnesium are added.
Flame retardant wires:
Definition: By adding a flame retardant (halogen-containing or halogen-free), the wire is flame-retardant, that is, the flame spread is limited after the fire source is withdrawn.
Material:
Halogen-containing flame retardant materials: such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC), neoprene rubber, etc., release hydrogen halide flame retardant when burned.
Halogen-free flame retardant materials: such as polyolefins (PE, EVA), phosphorus series flame retardants need to be added.
2. Combustion characteristics
Low smoke halogen-free wires:
Smoke volume: The amount of smoke during combustion is extremely low, with a light transmittance of ≥ 60%, ensuring visibility in a fire.
Toxicity: No toxic gases such as halogens are released, only a small amount of water mist is generated.
Flame retardancy: It has the ability to self-extinguish, but the flame retardant rating may be lower than that of halogen-containing flame retardant wires.
Flame retardant wires:
Flame retardant grades: divided into categories A, B, and C (GB/T 18380.3), with Class A having the strongest flame retardant performance.
Halogen-containing flame retardant wires: Good flame retardancy, but release toxic gases (such as HCl) when burned.
Halogen-free flame retardant wires: slightly less flame retardant, but low smoke content and non-toxic.
3. Environmental performance
Low smoke halogen-free wires:
Advantages: no halogen, low smoke, low toxicity, in line with environmental standards (such as ROHS), harmless to the environment and human body.
Application limitations: high cost, mainly used in places with high environmental requirements.
Flame retardant wires:
Halogen-containing flame retardant wires: poor environmental protection, generating toxic gases when burned.
Halogen-free flame retardant wires: Environmental protection is close to low-smoke halogen-free wires, but other flame retardants may be added.
4. Application scenarios
Low smoke halogen-free wires:
Mandatory scenarios: crowded public places (e.g. subways, airports, hospitals, schools).
Recommended scenarios: high-rise buildings, communication base stations, nuclear power plants, and other places with high safety requirements.
Flame retardant wires:
Ordinary flame retardant wires: homes, offices, and other general places.
High flame retardant wires: commercial buildings, industrial environments (e.g. chemical plants, oil platforms).
5. Industry standards
Low smoke halogen-free wires:
Halogen content: chlorine ≤ 50mg/g, bromine ≤ 10mg/g.
Combustion products: pH ≥ 4.3, conductivity ≤ 10 μS/mm (corrosion evaluation).
Light transmittance: smoke light transmittance ≥ 60%.
Flame retardant wires:
Flame retardant grade: GB/T 19666-2019 (A/B/C class), IEC 60332.
Test method: single vertical combustion, bundle combustion test.
summarize

Selection suggestion:
Preference is given to low-smoke halogen-free wires: public buildings, confined spaces, hospitals and schools, etc.
Flame retardant wires are suitable for general household or industrial environments (depending on the flame retardant grade).
 English
English  Spanish
Spanish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Arabic
Arabic  Russian
Russian  简体中文
简体中文 
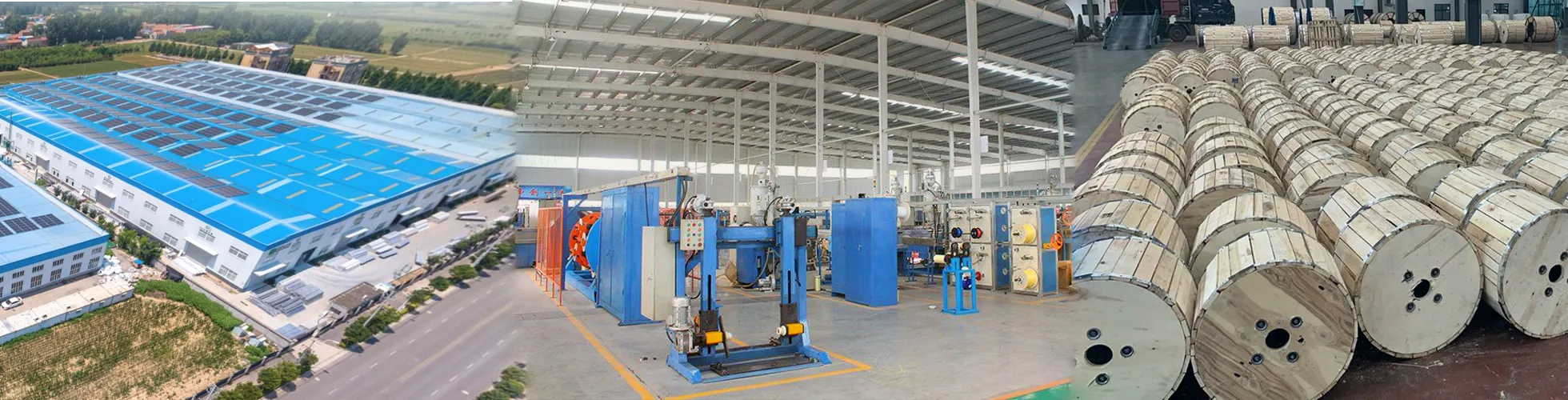


 Location:
Location: 

