The significance of several wires in the network cable
 Update Time:2025-12-14
Update Time:2025-12-14
 Traffic:
Traffic:
The eight wires in the network cable each bear different functions and roles. They together constitute the infrastructure of network communication and provide guarantees for the stable and reliable transmission of data. The following are the respective meanings of these eight wires:
First, send data line pair
Line 1: Send data signal (+)
In computer network communication, it is responsible for transmitting the positive polarity part of the data signal. This is one of the basic functions of realizing data transmission.
Line 2: Send data signal (-)
Used in combination with the first wire, it is responsible for transmitting the negative part of the data signal. This differential transmission method helps to reduce signal interference and improve data transmission quality.
Second, receive the data line pair
Line 3: Receive data signal (+)
The positive polarity part responsible for receiving data signals from the other device. Corresponds to the transmission line to ensure bidirectional data transmission.
Line 6: Receive data signal (-)
Used in combination with the 3rd wire, it is responsible for receiving the negative part of the data signal. This helps to ensure the integrity and accuracy of the received data signal.
III. Retention and backup lines
Line 4: Not widely used (but can be reserved for telephone use)
In some network configurations, the 4th cable may be used for telephone communication or other specific purposes. However, in most modern computer networks, it is usually not directly involved in data transmission.
Line 5: Not widely used (but can be retained)
Also, in most network configurations, it is not directly involved in data transmission and can exist as a redundant line or a backup line.
IV. Special function line
7th wire: ground wire
In computer network communication, the function of the grounding wire is to ensure the stability and security of the potential of the entire network. It helps to reduce electromagnetic interference and static accumulation and protect network equipment from damage.
Line 8: Not widely used (but can be paired with line 7 as a break or retention line)
In some special cases, the 8th line may be used together with the 7th line as an interrupt line or a reserved line to support a specific network function or configuration. However, in most cases, it is also not directly involved in data transmission.
It is worth noting that although not all wires are directly involved in data transmission in modern computer networks (especially the 4th, 5th, and 8th wires), they still play an important role in network communication. The use of these wires also follows specific wire sequence standards and specifications to ensure compatibility and interoperability between different devices.
In addition, different types of network cables also have different transmission capabilities. For example, Super Category 5 network cables are suitable for transmitting 100-megabit networks, while Category 6 network cables can easily handle the needs of gigabit networks. When choosing a network cable, you should make a reasonable choice according to the specific application scenarios and needs.
 English
English  Spanish
Spanish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Arabic
Arabic  Russian
Russian  简体中文
简体中文 
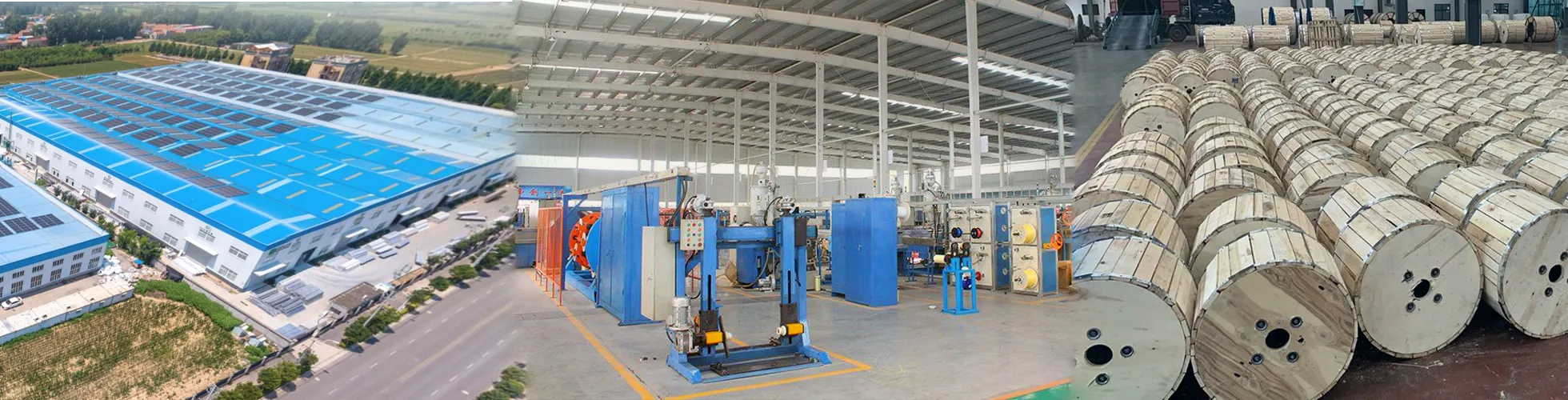


 Location:
Location: 

