(5)60 essential facts about optical fiber cables, save them and keep them with you!
 Update Time:2026-01-15
Update Time:2026-01-15
 Traffic:
Traffic:
43.What is the nonlinearity of optical fiber?
Answer: It means that when the input optical power exceeds a certain value, the refractive index of the optical fiber will be nonlinearly related to the optical power, and Raman scattering and Brillouin scattering will occur, causing the frequency of the incident light to change.
44.What impact does optical fiber nonlinearity have on transmission?
A: Nonlinear effects will cause some additional losses and interference, deteriorating the performance of the system. The optical power of the WDM system is large and is transmitted over a long distance along the optical fiber, so nonlinear distortion occurs. There are two types of nonlinear distortion: stimulated scattering and nonlinear refraction. Stimulated scattering includes Raman scattering and Brillouin scattering. The above two types of scattering reduce the energy of the incident light, causing loss. They can be ignored when the input fiber power is small.
45.What is PON (Passive Optical Network)?
Answer: PON is a fiber-optic loop optical network in the local user access network, based on passive optical devices such as couplers and splitters.
Various causes of fiber optic attenuation
Various causes of fiber optic attenuation
1. The main factors causing optical fiber attenuation are: intrinsic, bending, extrusion, impurities, unevenness and docking, etc.
Intrinsic: It is the inherent loss of optical fiber, including Rayleigh scattering, inherent absorption, etc.
Bending: When an optical fiber is bent, part of the light in the fiber will be lost due to scattering, causing loss.
Squeezing: Loss caused by tiny bends in the optical fiber when it is squeezed.
Impurities: Impurities in the optical fiber absorb and scatter the light propagating in the optical fiber, causing losses.
Inhomogeneity: Loss caused by the uneven refractive index of the optical fiber material.
Docking: Losses caused when optical fibers are docked, such as: different axes (the coaxiality requirement for single-mode optical fibers is less than 0.8 μm), the end face is not perpendicular to the axis, the end face is uneven, the docking core diameter does not match, and the fusion quality is poor.
When light enters from one end of an optical fiber and exits from the other end, the intensity of the light will weaken. This means that after the light signal propagates through the optical fiber, a part of the light energy is attenuated. This means that there are certain substances in the optical fiber or for some reason, blocking the light signal from passing through. This is the transmission loss of the optical fiber. Only by reducing the loss of the optical fiber can the optical signal pass unimpeded.
2. Classification of optical fiber loss
Optical fiber loss can be roughly divided into the inherent loss of the optical fiber and the additional loss caused by the use conditions after the optical fiber is manufactured. The specific breakdown is as follows:
Optical fiber loss can be divided into intrinsic loss and additional loss.
Intrinsic losses include scattering loss, absorption loss, and loss caused by imperfect optical fiber structure.
Additional losses include microbending losses, bending losses and splicing losses.
Among them, additional loss is artificially caused during the laying of optical fiber. In practical applications, it is inevitable to connect optical fibers one by one, and optical fiber connections will cause losses. Minor bending, squeezing, and stretching of optical fibers will also cause losses. These are all losses caused by the conditions under which optical fibers are used. The main reason is that under these conditions, the transmission mode in the optical fiber core changes. Additional loss can be avoided as much as possible. Below, we will only discuss the inherent loss of optical fiber.
Among the inherent losses, scattering loss and absorption loss are determined by the characteristics of the optical fiber material itself, and the inherent losses caused at different working wavelengths are also different. Understanding the mechanism of loss generation and quantitatively analyzing the magnitude of loss caused by various factors are extremely important for the development of low-loss optical fibers and the rational use of optical fibers.
 English
English  Spanish
Spanish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Arabic
Arabic  Russian
Russian  简体中文
简体中文 
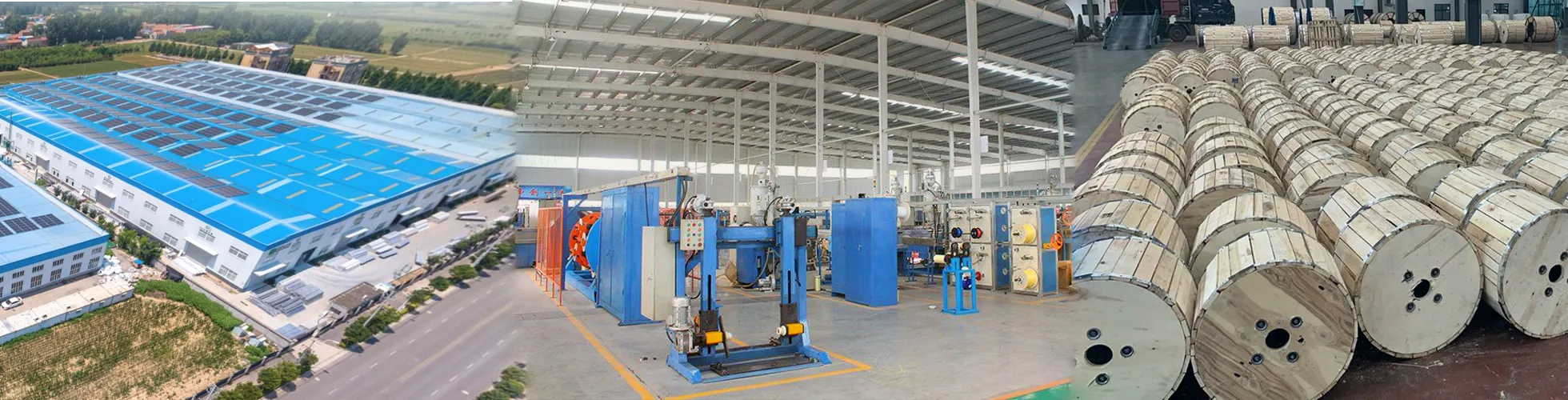


 Location:
Location: 

