what is fiber optic cable made of
 Update Time:2026-01-15
Update Time:2026-01-15
 Traffic:
Traffic:
Abstr: Fiber optic cables are crucial in the field of modern communications. This article will introduce the components of fiber optic cables in detail, including the core core, the protective cladding, as well as the strengthening elements that enhance mechanical properties and the sheath that provides physical protection, etc., so that readers can have a clear understanding of the composition of fiber optic cables.
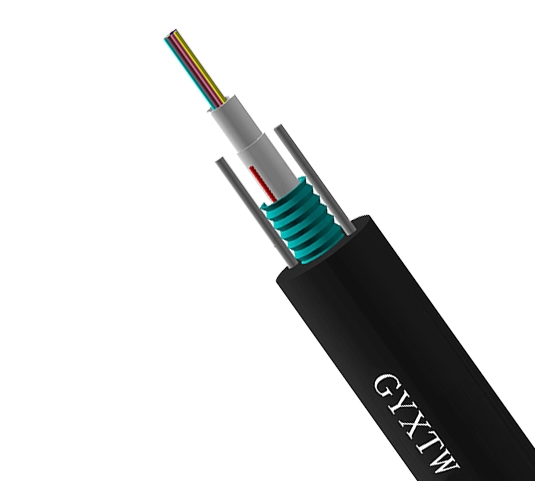

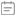
Fiber optic cable, component material, fiber core
Table of Contents:
-
core
-
cladding
-
reinforcement element
-
sheath
In today's highly developed information age, fiber optic cables undoubtedly play an extremely important role. As a key medium for information transmission, it carries massive amounts of data and signals, enabling us to achieve fast and stable communication. So, what exactly is fiber optic cable made of?
core
The core is the core part of a fiber optic cable. It is usually made of high-purity silicon dioxide (SiO 2). Its main function is to conduct light signals. Silicon dioxide is a very common inorganic material that is widely found in nature. In order to change the refractive index of the core so that it can effectively guide light to propagate in it, a small amount of other materials such as germanium, phosphorus, etc. are usually added to the silica. The proportion of these additives is precisely controlled according to the specific design requirements to ensure that the core has suitable optical characteristics. The diameter of the core is usually very small. The core diameter of single-mode fiber is generally around 8-10 microns, while the core diameter of multimode fiber is relatively large, between 50-62.5 microns.
Cladding
The cladding is wrapped around the outside of the core and is also made of silica, but its refractive index is lower than that of the core. This difference in refractive index is the key to the propagation of light in the core through total reflection. The existence of the cladding is like a "track" for the light signal, allowing the light to move along the direction of the core without leaking out easily. The thickness of the cladding is generally around 125 microns, which is a standard size that ensures the basic performance and compatibility of the optical fiber.
Reinforcement elements
Since the optical fiber itself is relatively fragile and susceptible to stretching and bending, reinforcement elements need to be added to improve the mechanical properties of the optical fiber cable. Common reinforcement elements include steel wire, aramid fiber, etc. Steel wire has high strength and rigidity, can effectively withstand tensile force, and protect the optical fiber from being broken. Aramid fiber is a high-performance organic fiber that has the characteristics of light weight and high strength. It also has good flexibility and can resist bending stress to a certain extent. Reinforcement elements are usually distributed around the optical fiber. Depending on the design and application scenarios of the cable, their number and arrangement will vary.
Sheath
The sheath is the outermost structure of the optical fiber cable. Its main function is to provide physical protection for the internal optical fiber and reinforcement components to prevent them from being affected by the external environment, such as mechanical damage, chemical corrosion, moisture intrusion, etc. There are many kinds of sheath materials, the most common ones are polyethylene (PE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), etc. Polyethylene has good chemical corrosion resistance and weather resistance, and can be used in various harsh environmental conditions. Polyvinyl chloride has high wear resistance and flame retardancy, and is suitable for some occasions with high fire protection requirements. In addition, according to different application requirements, other special materials or structures such as waterproof tape and shielding layer can be added to the sheath to further improve the performance of the cable.
In addition to the above main parts, some special optical fiber cables may also contain filling materials, buffer layers and other structures. Filling materials are usually used to fill the gaps inside the cable to prevent moisture and impurities from entering, and can also play a certain buffering role. The buffer layer can further protect the optical fiber and reduce the impact of external stress on the optical fiber.
In short, optical fiber cables are composed of multiple parts such as core, cladding, reinforcement elements, and sheaths, each of which has unique functions and material choices. It is these carefully designed and combined parts that enable fiber optic cables to transmit optical signals stably and efficiently in complex environments, providing a solid foundation for our modern communication life.
 English
English  Spanish
Spanish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Arabic
Arabic  Russian
Russian  简体中文
简体中文 


 Location:
Location: 

