(2)60 essential facts about optical fiber and cables, save them and keep them with you!
 :2025-12-13
:2025-12-13
 :
:
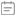
11.What is the backscattering method?
A: The backscattering method is a method for measuring attenuation along the length of an optical fiber. Most of the optical power in the optical fiber propagates forward, but a small part is backscattered toward the light emitter. Using a spectrometer at the light emitter to observe the time curve of backscattering, not only can the length and attenuation of the connected uniform optical fiber be measured from one end, but also local irregularities, breakpoints, and optical power loss caused by joints and connectors can be measured.
OTDR uses backscattering to measure the loss and length of optical cable lines.
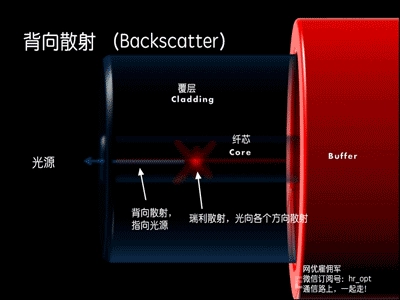
12.What is the testing principle of Optical Time Domain Reflectometer (OTDR)? What are its functions?
A: OTDR is based on the principle of light backscattering and Fresnel reflection. It uses the backscattered light generated when light propagates in the optical fiber to obtain attenuation information. It can be used to measure optical fiber attenuation, joint loss, optical fiber fault point location, and understand the loss distribution along the length of the optical fiber. It is an indispensable tool in optical cable construction, maintenance and monitoring. Its main indicators include: dynamic range, sensitivity, resolution, measurement time and blind area.
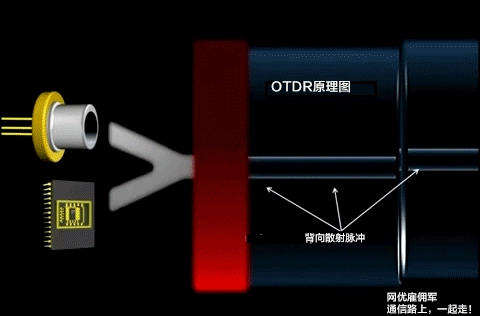
13.What is the blind area of OTDR? What is the impact on the test? How to deal with the blind area in actual testing?
Answer: The series of "blind spots" caused by saturation of the OTDR receiving end due to reflections generated by characteristic points such as active connectors and mechanical joints are usually called blind areas.
The blind areas in optical fibers are divided into event blind areas and attenuation blind areas. The length from the starting point of the reflection peak caused by the intervention of active connectors to the receiver saturation peak is called the event blind area. The length from the starting point of the reflection peak to other identifiable event points caused by the intervention of active connectors in optical fibers is called the attenuation blind area.
For OTDR, the smaller the blind area, the better. The blind area will increase with the increase of pulse width. Although increasing the pulse width increases the measurement length, it also increases the measurement blind area. Therefore, when testing optical fiber, narrow pulses should be used to measure the optical fiber attached to the OTDR and the adjacent event points, while wide pulses should be used to measure the far end of the optical fiber.
14.Can OTDR measure different types of optical fibers?
A: If you use a single-mode OTDR module to measure a multimode fiber, or use a multimode OTDR module to measure a single-mode fiber with a core diameter of 62.5 mm, the measurement result of the fiber length will not be affected, but the results of fiber loss, optical connector loss, and return loss will be incorrect. Therefore, when measuring optical fiber, you must select an OTDR that matches the fiber being measured to obtain correct results for all performance indicators.
15.What does "1310nm" or "1550nm" mean in common optical test instruments?
A: It refers to the wavelength of the optical signal. The wavelength range used in optical fiber communication is in the near-infrared region, between 800nm and 1700nm. It is often divided into short wavelength band and long wavelength band, the former refers to 850nm wavelength, and the latter refers to 1310nm and 1550nm.
 English
English  Spanish
Spanish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Arabic
Arabic  Russian
Russian  简体中文
简体中文 


 :
: 

