(7)60 essential facts about optical fiber cables, save them and keep them with you!
 Update Time:2025-12-12
Update Time:2025-12-12
 Traffic:
Traffic:
Fiber loss In recent years, fiber optic communication has been widely used in many fields. To achieve fiber optic communication, an important issue is to reduce the fiber loss as much as possible. The so-called loss refers to the attenuation of the fiber per unit length, and the unit is dB/km. The level of fiber loss directly affects the transmission distance or the distance between relay stations. Therefore, understanding and reducing the fiber loss has great practical significance for fiber optic communication.
1. Optical fiber absorption loss
This is caused by the absorption of light energy by the optical fiber material and impurities. They consume light energy in the form of heat energy in the optical fiber, which is an important loss in optical fiber loss. Absorption loss includes the following:
1. Material intrinsic absorption loss This is the loss caused by the intrinsic absorption of the material. It has two bands, one in the near-infrared 8-12μm region, the intrinsic absorption of this band is due to vibration. The other material intrinsic absorption band is in the ultraviolet band, when the absorption is very strong, its tail will be dragged to the 0.7-1.1μm band.
2. Absorption loss caused by dopants and impurity ions Optical fiber materials contain transition metals such as iron, copper, chromium, etc. They have their own absorption peaks and absorption bands and vary with their valence states. The optical fiber loss caused by the absorption of transition metal ions depends on their concentration. In addition, the presence of OH- also produces absorption loss. The basic absorption peak of OH- is near 2.7μm, and the absorption band is in the range of 0.5 to 1.0μm. For pure quartz optical fiber, the loss caused by impurities can be ignored.
3. Atomic defect absorption loss When the optical fiber material is heated or strongly radiated, it will be stimulated to produce atomic defects, resulting in absorption of light and loss, but in general this effect is small.
2. Scattering loss of optical fiber
Scattering inside the optical fiber will reduce the transmitted power and cause loss. The most important scattering is Rayleigh scattering, which is caused by changes in density and composition inside the optical fiber material.
During the heating process of optical fiber materials, due to thermal agitation, the compressibility of atoms is uneven, the density of the material is uneven, and the refractive index is uneven. This unevenness is fixed during the cooling process, and its size is smaller than the wavelength of light. When light encounters these uneven materials with random fluctuations that are smaller than the wavelength of light during transmission, the transmission direction is changed, scattering occurs, and loss occurs. In addition, uneven concentration of oxides and uneven doping in optical fibers can also cause scattering and loss.
3. Waveguide Scattering Loss
This is due to the scattering caused by random distortion or roughness of the interface. In fact, it is mode conversion or mode coupling caused by surface distortion or roughness. Due to the fluctuation of the interface, one mode will produce other transmission modes and radiation modes. Since the attenuation of various modes transmitted in the optical fiber is different, in the process of long-distance mode conversion, the mode with low attenuation becomes the mode with high attenuation. After continuous conversion and reverse conversion, although the loss of each mode will be balanced, the mode as a whole will produce additional loss, that is, additional loss is generated due to mode conversion. This additional loss is the waveguide scattering loss. To reduce this loss, it is necessary to improve the optical fiber manufacturing process. For well-drawn or high-quality optical fibers, this loss can basically be ignored.
4. Radiation loss caused by optical fiber bending
Optical fiber is soft and can be bent. However, after being bent to a certain degree, although the optical fiber can guide light, the transmission path of light will be changed. The transmission mode is converted to the radiation mode, so that part of the light energy penetrates into the cladding or passes through the cladding to become the radiation mode and leaks outward, thus generating loss. When the bending radius is greater than 5 to 10 cm, the loss caused by bending can be ignored.
 English
English  Spanish
Spanish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Arabic
Arabic  Russian
Russian  简体中文
简体中文 
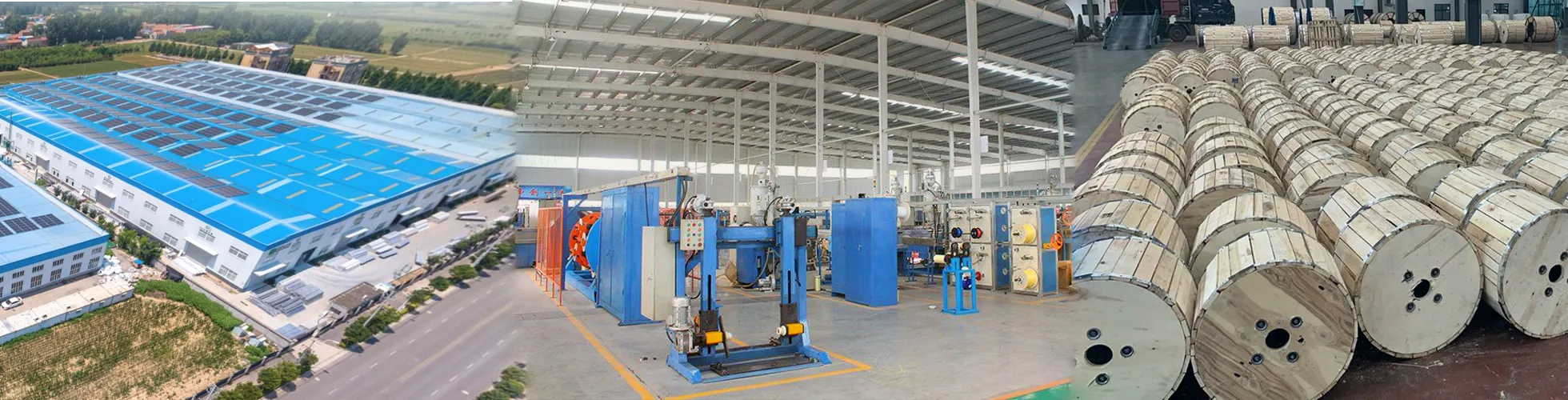


 Location:
Location: 

